Comparison Of MIG Welding And TIG Welding(2)
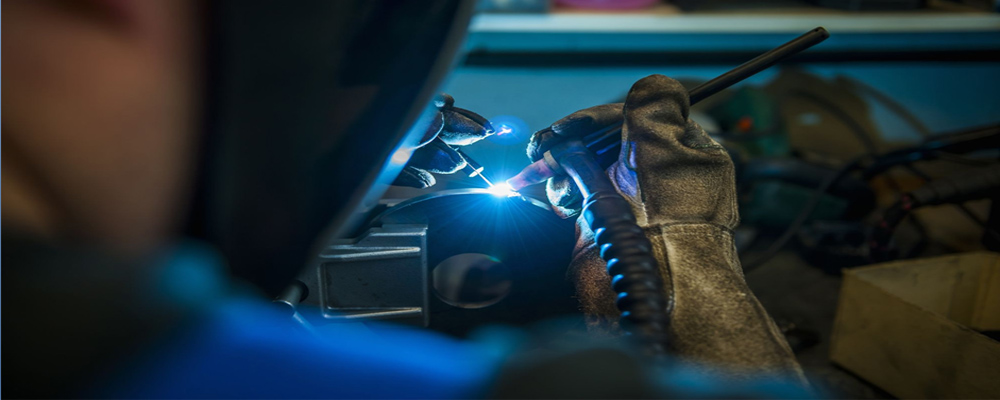

The correct connection of the welder is that the workpiece is connected to the positive pole of the power supply, and the tungsten pole in the torch acts as the negative pole. The inert gas is typically argon. The inert gas is fed through the torch to form a shield around the arc and on the weld pool. To increase the heat input, typically 5% hydrogen is added to the argon. However, when ferritic stainless steel is welded, it cannot be hydrogenated in argon. Gas consumption is about 3 to 8 liters per minute. In addition to the inert gas being blown from the torch during the welding process, it is preferable to blow the gas for protecting the back of the weld from the weld.
If necessary, the weld pool can be filled with the same wire as the austenitic material being welded. When welding ferritic stainless steel, type 316 is usually used. Due to the protection of argon gas, the harmful effect of air on molten metal is isolated. Therefore, TIG welding is widely used for welding non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, magnesium and other alloys, stainless steel, high-temperature alloy, titanium and titanium alloy which are easily oxidized. Fused active metals (such as molybdenum, niobium, zirconium, etc.), and general carbon steel, low alloy steel and other common materials, in addition to high welding quality requirements, generally do not use TIG welding.
Related Products
Contact Us
Please feel free to let us know your demand information, we will contact you as soon as possible, looking forward to cooperate with you!